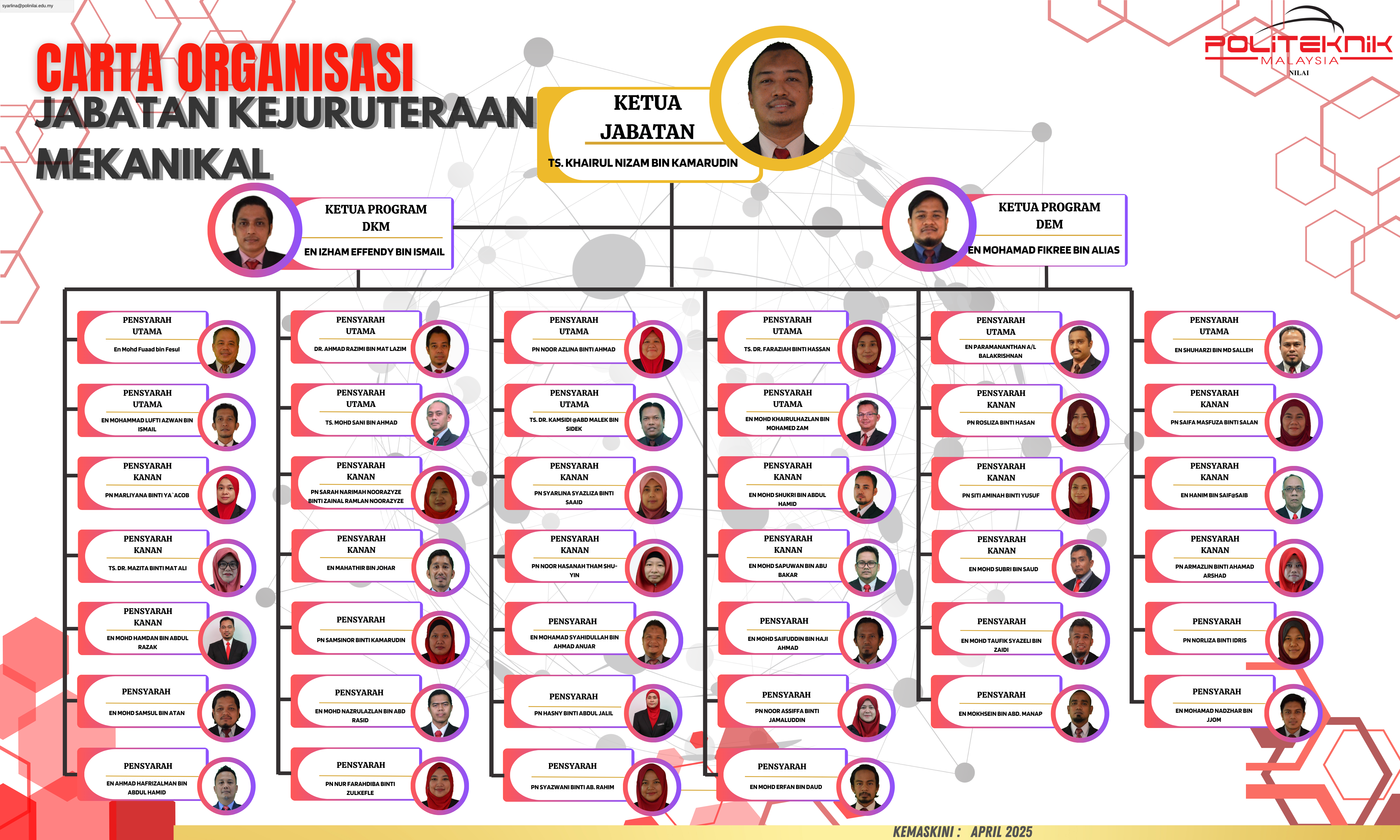
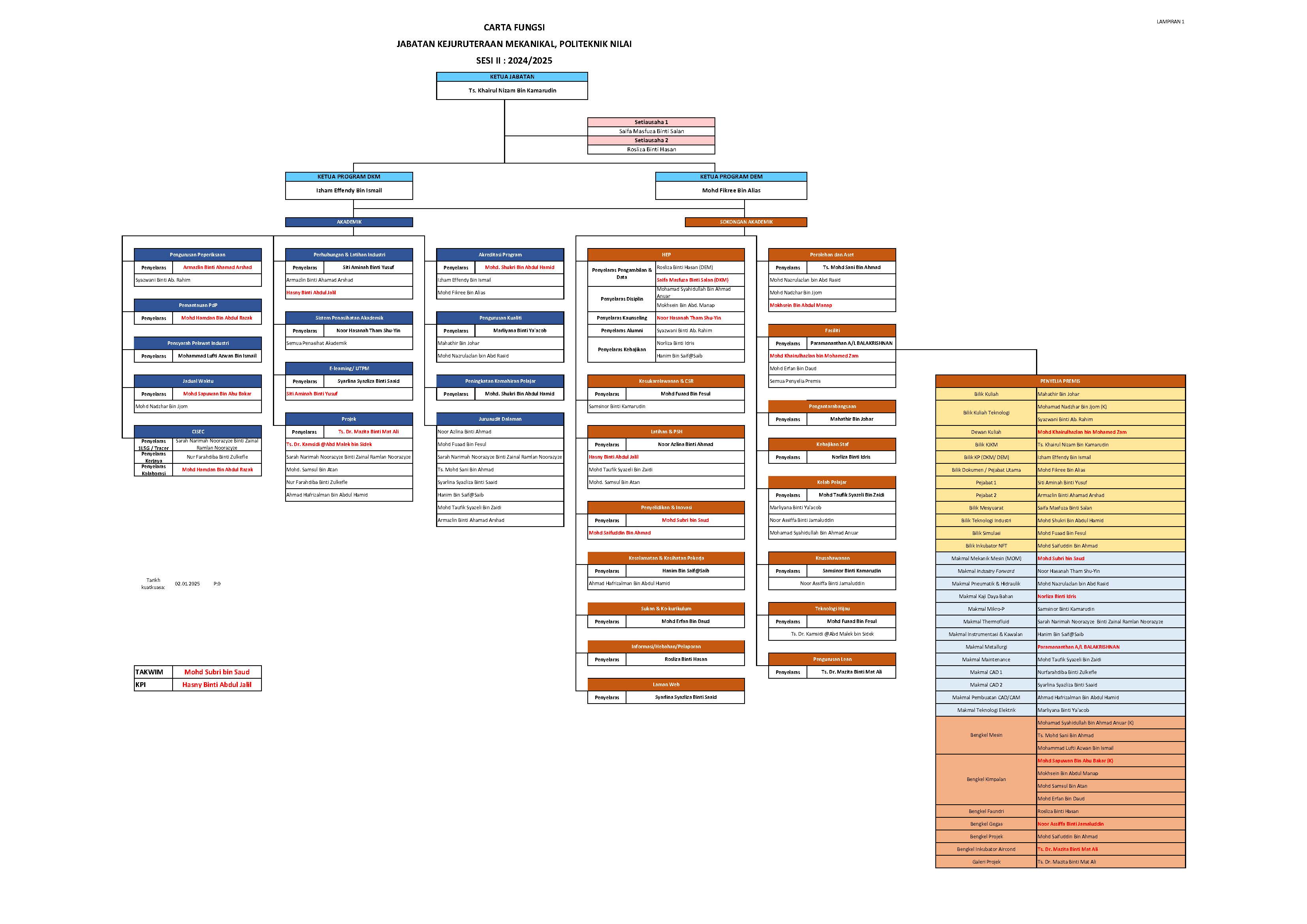
Objektif Jabatan
Objektif
Sekurang-kurangnya 25% daripada pelajar yang lulus mencapai PNM 3.00 atau lebih untuk setiap program bagi setiap semester.
VISI
Menjadi pusat kecemerlangan Pendidikan dan latihan dalam bidang Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan berazam melahirkan graduan yang berketrampilan dalam aspek ilmu, kemahiran dan akhlak selari dengan Falsafah Pendidikan Kebangsaan.
MISI
Memenuhi keperluan negara dalam bidang kejuruteraan dengan menghasilkan tenaga kerja separa professional yang berkualiti.
Sinopsis DKM
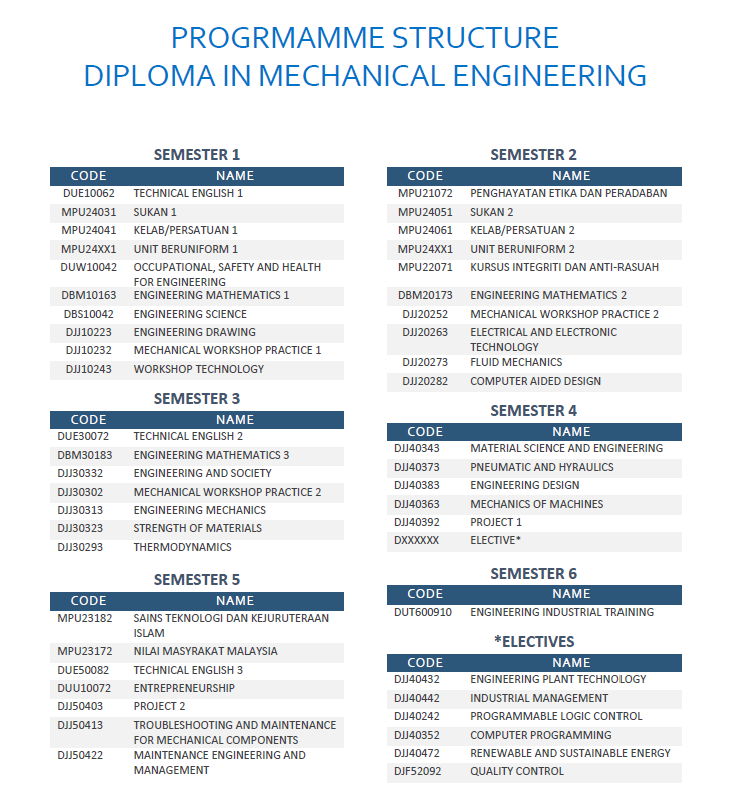
DIPLOMA IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (DKM)INTRODUCTION The New Industrial Master Plan 2030 (NIMP 2030) targets to build Malaysia's industrial capacity and resilience for long-term and sustainable growth. NIMP 2030 is designed to drive Malaysia’s trajectory as a global leader in industrial development, extend the domestic linkages to create wealth across the nation as well as strengthen its position in the global value chain. Three key global trends are; first is leverage mature industrial infrastructure with good connectivity, strategic location and reputation. Second, step up efforts to develop high-skilled talent and enhance TVET programmes. Third, to create new growth opportunities in green manufacturing, electric vehicles, and carbon capture, utilisation, and storage (CCUS). NIMP 2030 missions have been formulated to drive industry transformation at a large scale: to advance economic complexity, to tech up for a digitally vibrant nation, to push for net zero, to safeguard economic security and inclusivity. The Twelfth Malaysia Plan (12MP) policy improving the educational ecosystem and technical and vocational training (TVET) to develop talent available time the front will be known as the driver changes to meet demand industry better. Industry 4.0 refers to the intelligent networking of machines and processes using information and communication technology (ICT). Industry 4.0 transforms manufacturing processes from product design to fabrication, operation, and maintenance. It fosters automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies and processes through physical-cyber systems. Industry 4.0, a subset of the 4IR, focuses on the manufacturing sector, whereas 4IR encompasses almost every industry and all aspects of human life. Diploma in Mechanical Engineering for polytechnic is developed to give balance emphasis on theoretical and practical aspects. Thus, to keep abreast with rapid demand in TVET sector, Department of Polytechnic and Community College Education (DPCCE) progressively collaborates with major industry players in the country in developing the curriculum. The Diploma in Mechanical Engineering programme will take six semesters to complete, five academic semesters at their respective polytechnics and one semester of industrial training at relevant industries during the final semester. This programme complies with the Malaysian Qualifications Agency (MQA) and Board of Engineer Malaysia (BEM) /Engineering Technology Accreditation Council (ETAC). SYNOPSIS The Diploma in Mechanical Engineering programme is designed to produce holistic graduates that have knowledge and competent skills in the field of mechanical engineering to fulfil the demand of workers in engineering sector. The programme structure focuses on the area of Solid Mechanics, Statics & Dynamics, Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics, Materials, Mechanical Design, Workshop Practices, Manufacturing, Instrumentation & Control, Mechanical Maintenance, Electrical & Electronic Technology and Computer Programming. JOB PROSPECT This programme provides the knowledge and skills in Mechanical Engineering field that can be applied to a broad range of careers in Mechanical Engineering. The knowledge and skills that the students acquire from the programme will enable them to participate in the job market as:
DEPARTMENT OF POLYTECHNIC AND COMMUNITY COLLEGE EDUCATION VISION To be the Leading-Edge TVET Institution DEPARTMENT OF POLYTECHNIC AND COMMUNITY COLLEGE EDUCATION MISSION To provide wide access to quality and recognized TVET programmes
EDUCATIONAL GOAL To produce holistic and competent TVET graduates capable of contributing to the national development. PROGRAMME AIM The programme believes that every individual has potential, and the programme aims to develop adaptable and responsible Senior Assistant Engineers to support government aspiration to increase workforce in engineering related field. PROGRAMME EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES (PEO) Within a few years after completing Diploma in Mechanical Engineering, graduates are able to: PEO1: proficient with industry-relevant knowledge and skills in mechanical engineering field PEO2: engaging on lifelong and continuous learning to enhance knowledge and skills PEO3: acquire with entrepreneurial skills and mind set in the real working environment PEO4: establish links with society and players in the industry PROGRAMME LEARNING OUTCOMES (PLO) Upon completion of the programme, students should be able to: PLO 1: apply knowledge of applied mathematics, applied science, computer and engineering fundamentals and an engineering specialisation as specified in DK1 to DK4 respectively to wide practical procedures and practices in area of mechanical engineering. PLO 2: identify and analyse well-defined engineering problems reaching substantiated conclusions using codified methods of analysis specific to mechanical engineering field (DK1 to DK4). PLO 3: design solutions for well-defined technical problems and assist with the design of systems, components or processes to meet specified needs with appropriate consideration for public health and safety as well as, cultural, societal and environmental considerations in area of mechanical engineering (DK5). PLO 4: conduct investigations of well-defined problems; locate and search relevant codes and catalogues, conduct standard tests and measurements (DK8). PLO 5: apply appropriate techniques, resources, and modern engineering computing and IT tools to well-defined engineering problems, with an awareness of the limitations (DK2 and DK6). PLO 6: consider sustainable development impacts* to: society, the economy, sustainability, health and safety, legal frameworks, and the environment, in solving well- defined engineering problems (DK1, DK5 and DK7). PLO 7: understand and commit to professional ethics and responsibilities and norms of technician practice and including compliance with national and international laws. Demonstrate an understanding of the need for diversity and inclusion (DK9). PLO 8: function effectively as an individual, and as a member in diverse and inclusive teams in multi-disciplinary, face-to-face, remote and distributed settings (DK9). PLO 9: communicate effectively and inclusively on well-defined engineering activities with the engineering community and with society at large, by being able to comprehend the work of others, document their own work, and give and receive clear instructions. PLO 10: demonstrate awareness of engineering management principles as a member or leader in a technical team and to manage projects in multidisciplinary environments. PLO 11: recognise the need for, and have the ability for i) independent and lifelong learning and ii) critical thinking in the face of specialised technical knowledge (DK8). *Represented by the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals (UN-SDG). Notes: DK 1: A descriptive, formula-based understanding of the natural sciences applicable in a sub-discipline and awareness of directly relevant social sciences. DK 2: Procedural mathematics, numerical analysis, statistics applicable in a sub- discipline. DK 3: A coherent procedural formulation of engineering fundamentals required in an accepted sub-discipline. DK 4: Engineering specialist knowledge that provides the body of knowledge for an accepted sub-discipline. DK 5: Knowledge that supports engineering design and operations based on the techniques and procedures of a practice area. DK 6: Codified practical engineering knowledge in recognized practice area. DK 7: Knowledge of issues and approaches in engineering technician practice, such as public safety and sustainable development. DK 8: Engagement with the current technological literature of the practice area. DK 9: Knowledge of professional ethics, responsibilities, and norms of engineering practice. Awareness of the need for diversity by reason of ethnicity, gender, age, physical ability etc. with mutual understanding and respect, and of inclusive attitudes. DK: Knowledge Profile Dublin Knowledge refers to the Knowledge Profile as listed in the Manual of Engineering Technician Education Programme Accreditation Standard (ETAC) for diploma programmes. |
Sinopsis DEM
DIPLOMA IN MECHATRONIC ENGINEERING (DEM)INTRODUCTION Industry 4.0 aims to optimise what has been done in Industry 3.0. Industry 4.0 which originates from Germany’s ‘Industrie 4.0’, which refers to the intelligent networking of machines and processes using Information and Communication technology (ICT). Industry 4.0 transforms manufacturing processes from product design to fabrication, operation and maintenance. It fosters automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies and processes through physical-cyber systems. Industry 4.0 is a subset of the 4IR which focuses on the manufacturing sector, whereas 4IR encompasses almost every industry and all aspects of human life. The Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) is a fusion of technologies, which cuts across the physical, digital and biological worlds. It evolves exponentially as a result of the multifaceted, deeply interconnected world we live in. Emerging fields of knowledge continue to produce newer and ever more capable technology. In line with the 3rd Industrial Malaysia Plan (IMP3) aiming for the innovative and creative human capital development, via matching talent to expertise with market demand, Diploma in Mechatronic Engineering for polytechnic is developed to provide balance emphasis on theoretical and practical aspects. The Eleventh Malaysia Plan was drawn to produce 60% out of 1.5 million workers in the TVET sector. Until now a total of 69,475 (51%) of the 136,062 technical education and vocational training (TVET) graduates in Malaysia are working as professionals and skilled workers. Hence, Department of Polytechnic and Community College Education (DPCCE) progressively collaborates with major industry players in the country in developing the curriculum to keep up with rapid demand in TVET sector. The programme will take six semesters to complete, five academic semesters at their respective polytechnics and one semester of industrial training at relevant industries during the final semester. This programme complies with the Board of Engineer (BEM) requirement. SYNOPSIS The Diploma in Mechatronic Engineering programme is designed to produce holistic graduates that possess knowledge and competent skills in the field of mechatronic engineering to fulfil the demand of workers in the engineering sector. Five components related to the program have been identified. Components which make up the BOK for Diploma in Mechatronic Engineering are namely Technical, Personal Development, Mathematics, Science and Workplace Competencies. Technical Components is Electronics, Industrial Electronics, Electrical, Computer Aided Design, C Programming, Pneumatic and Hydraulics, Programmable Logic Controller, Safety, Power Electronics, Embedded System Applications, Control System and Industrial Automation. JOB PROSPECT This programme provides the knowledge and skills in Mechatronic Engineering field that can be applied to a broad range of careers in Mechatronic Engineering. The knowledge and skills that the students acquire from the programme will enable them to participate in the job market as:
DEPARTMENT OF POLYTECHNIC AND COMMUNITY COLLEGE EDUCATION VISION To be the Leading-Edge TVET Institution DEPARTMENT OF POLYTECHNIC AND COMMUNITY COLLEGE EDUCATION MISSION
EDUCATIONAL GOAL To produce holistic and competent TVET graduates capable of contributing to the national development. PROGRAMME AIM The programme believes that every individual has potential and the programme aims to develop adaptable and responsible Senior Assistant Mechatronic Engineers to support governments aspiration to increase workforce in engineering related fields. PROGRAMME EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES (PEO) Within a few years after completing Diploma in Mechatronic Engineering, graduates are able to: PEO1: proficient with industry-relevant knowledge and skills in mechatronic engineering field PEO2: engaging on lifelong and continuous learning to enhance knowledge and skills PEO3: acquire with entrepreneurial skills and mindset in the real working environment PEO4: establish links with society and players in the industry PROGRAMME LEARNING OUTCOMES (PLO) Upon completion of the programme, students should be able to: PLO 1: apply knowledge of applied mathematics, applied science, computer and engineering fundamentals and an engineering specialisation as specified in DK1 to DK4 respectively to wide practical procedures and practices in area of mechatronic engineering. PLO 2: identify and analyse well-defined engineering problems reaching substantiated conclusions using codified methods of analysis specific to mechatronic engineering field (DK1 to DK4). PLO 3: design solutions for well-defined technical problems and assist with the design of systems, components or processes to meet specified needs with appropriate consideration for public health and safety as well as, cultural, societal, and environmental considerations in area of mechatronic engineering (DK5). PLO 4: conduct investigations of well-defined problems; locate and search relevant codes and catalogues, conduct standard tests and measurements (DK8). PLO 5: apply appropriate techniques, resources, and modern engineering computing and IT tools to well-defined engineering problems, with an awareness of the limitations (DK2, DK6). PLO 6: consider sustainable development impacts* to: society, the economy, sustainability, health and safety, legal frameworks, and the environment, in solving well-defined engineering problems (DK1, DK5, DK7). PLO 7: understand and commit to professional ethics and responsibilities and norms of technician practice and including compliance with national and international laws. Demonstrate an understanding of the need for diversity and inclusion (DK9). PLO 8: function effectively as an individual, and as a member in diverse and inclusive teams in multi-disciplinary, face-to-face, remote and distributed settings (DK9). PLO 9: communicate effectively and inclusively on well-defined engineering activities with the engineering community and with society at large, by being able to comprehend the work of others, document their own work, and give and receive clear instructions. PLO 10: demonstrate awareness of engineering management principles as a member or leader in a technical team and to manage projects in multidisciplinary environments. PLO 11: recognise the need for, and have the ability for i) independent and lifelong learning and ii) critical thinking in the face of specialised technical knowledge (DK8). *Represented by the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals (UN-SDG). Notes: DK 1: A descriptive, formula-based understanding of the natural sciences applicable in a sub-discipline and awareness of directly relevant social sciences. DK 2: Procedural mathematics, numerical analysis, statistics applicable in a sub- discipline. DK 3: A coherent procedural formulation of engineering fundamentals required in an accepted sub-discipline. DK 4: Engineering specialist knowledge that provides the body of knowledge for an accepted sub-discipline. DK 5: Knowledge that supports engineering design and operations based on the techniques and procedures of a practice area. DK 6: Codified practical engineering knowledge in recognized practice area. DK 7: Knowledge of issues and approaches in engineering technician practice, such as public safety and sustainable development. DK 8: Engagement with the current technological literature of the practice area. DK 9: Knowledge of professional ethics, responsibilities, and norms of engineering practice. Awareness of the need for diversity by reason of ethnicity, gender, age, physical ability etc. with mutual understanding and respect, and of inclusive attitudes. DK: Knowledge Profile Dublin Knowledge refers to the Knowledge Profile as listed in the Manual of Engineering Technician Education Programme Accreditation Standard (ETAC) for diploma programmes. |
Lembaga Jurutera Malaysia
Lembaga Jurutera Malaysia (BEM)
Lembaga Jurutera Malaysia (BEM) adalah badan berkanun yang dibentuk di bawah Akta Pendaftaran Jurutera 1967 (REA 1967). BEM adalah sebuah badan kerajaan yang bertanggungjawab untuk mengurus pendaftaran jurutera di Malaysia dan mengawal selia kod/amalan jurutera berdaftar. Tujuannya adalah untuk melindungi keselamatan dan kepentingan awam di Malaysia.
Peranan utama BEM adalah untuk memudahkan pendaftaran Jurutera, Teknologis Kejuruteraan, Inspektor Kerja, Pemilikan Tunggal, Perkongsian dan Badan Korporat dan menyediakan perkhidmatan kejuruteraan profesional untuk mengawal selia tingkah laku profesional dan amalan orang berdaftar untuk menjaga keselamatan dan kepentingan orang ramai.
|
NO |
SITE |
LINK |
|
1 |
BEM Official Website |
|
|
2 |
Mandatory Registration with the Board of Engineers Malaysia |
|
|
3 |
BEM Mini Convention Presentation Material |
|
|
BEM Webinar Presentation Material |
||
|
5 |
BEM Official Youtube Channel |
IAP
PANEL PENASIHAT INDUSTRI (PPI) 2024
INDUSTRIAL ADVISORY PANEL (IAP) 2024
Pengenalan
Sebagai langkah untuk memperkukuhkan hubungan Politeknik dengan industri dalam akademik dan aktiviti kolaborasi, Panel Penasihat Industri (PPI) telah ditubuhkan untuk:
- Membantu program mengenalpasti potensi dari segi penyelidikan dan pembangunan projek akhir.
- Mengadakan sesi perkongsian ilmu bersama staf dan pelajar bagi meningkatkan kefahaman tentang bidang pengkhususan program mekanikal dan mekatronik yang berkaitan.
- Maklumbalas keberkesanan kursus Diploma Kejuruteraan Mekanikal dan Diploma Kejuruteraan Mekatronik.
|
BIL |
NAMA |
JAWATAN |
ORGANISASI |
|
1 |
En Mohamad Sabri Bin Othman |
Pengarah |
USS ENGINEERING & TRADING Kawasan Industri Mara (KIM) W/P,Lot A33, KM13, Off Jalan Batu Caves,68100 Batu Caves,Kuala Lumpur. |
|
2 |
En Mohamad Ariffin Bin Zulkifli |
Pengarah Urusan |
MYINVENT TECHNOLOGIES SDN BHD 7A, Jalan Badminton 13/29,Tadisma Business Park,40100 Shah Alam,Selangor |
|
3 |
En Melvin Lim Chun Hean |
Managing Director |
GENTLE AUTOMATIC SOLUTION SDN BHD 36, Jalan Industri USJ 1/13,Taman Perindustrian USJ 1,47600 Subang Jaya,Selangor Website: www.gentle.com.my |
|
4 |
En Nasrizal Bin Mohd. Noor |
General Manager |
TEKNIK BEKAL TECHNOLOGY SDN BHD 7, Jalan Nilai 2,Taman Perindustrian Teknologi Tinggi,47500 Subang Jaya,Selangor Website: https://alirantenaga.com.my |
|
5 |
En Wan Halmy Bin Wan Yusup |
Ketua Pegawai Eksekutif |
STRADA RESOURCES No. 475-1, Jalan Bandar Senawang 18,Pusat Bandar Senawang,70450 Senawang,Negeri Sembilan. |